
Damage protective vegetation.Ĭlimate change driven rising temperatures, changes in rainfall patterns and an increase in extreme weather events threatens fodder crop production. Increased or decreased water balances within landscapes. Increases or decreases in the amount of rainfall and solar energy available on a regional/local basis. Increases or decreases in water balance at a local and regional scale

More unstable precipitation patterns and increases in global temperature. Warmth favours chemical weathering over physical, leading to deeper weathering. Low temperatures cause slow rates of chemical weathering and rely on physical processes. Increased or decreased quality of seed dispersal through windĪlteration of biochemical and chemical reactions.īiochemical reactions involved in decomposition and fixation processes are temperature dependent and have high temperature sensitivity. Increases or decreases in wind velocity on a local basis Increases or decreases in dispersal distance through wind. Droughts may cause disruption of water for sound attenuation. an El Niño is associated with warm and very wet weather months in April–October causing major flooding in southern hemisphere countries such as Peru and Ecuador.Īlters conditions: temperature, humidity, rainfall.Ĭlimatic conditions affect air pollution levels and absorption by vegetation. Regulation of regional climate is heavily impacted, e.g. ENSO) create deficits and excesses in temperature and precipitation. Prolonged periods of high pressure with little air movement can lead to temperature inversions (reversal of the normal decrease of air temperature with altitude).ĭecrease in air flow reduces dilution effect and leads to accumulation of dust and pollutants.Ĭlimatic anomalies (e.g.
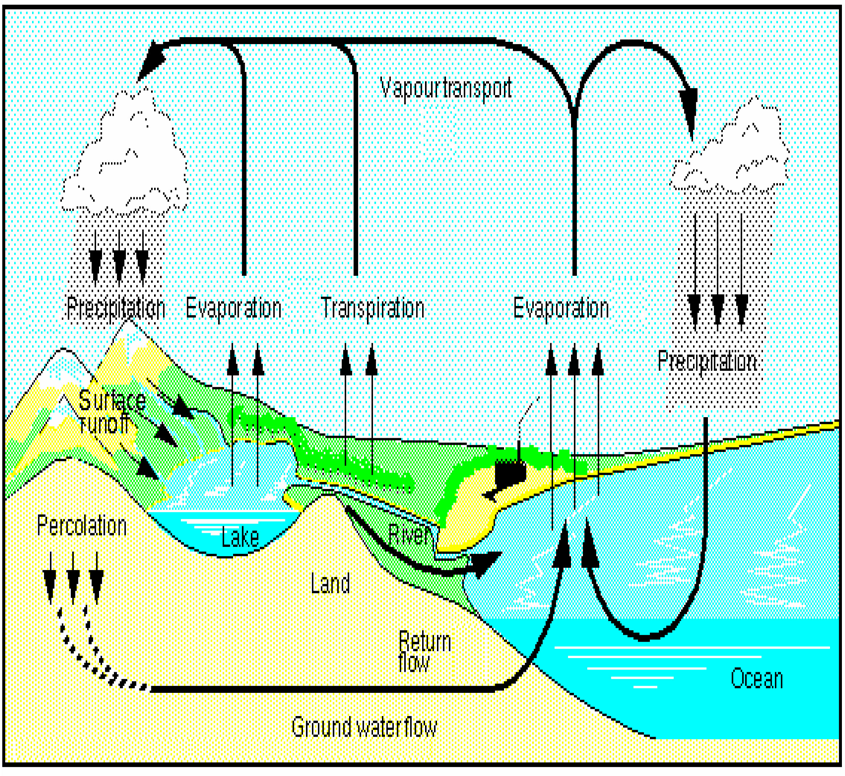
Increased or decreased availability of water at the local and landscape level. Type of land use determines type of disturbance (tillage, agrochemicals, fertilizers, excrements, etc.) changes soil properties.Ĭhanges to the way water flows through landscapes Vegetation alteration can degrade or cause loss of service.ĭeforestation, loss of biological community.Īlters biological, mechanical and chemical weathering processes. 5-8 % of global crop production would be lost if pollination services ceased. spring for most crops in temperate zones). Altered wind and hydrological processes within a given area will affect how far seeds are dispersed.ĭeclines in pollinator populations due to reduced access to food and nesting resources (16.5 % of vertebrate pollinator species are threatened with global extinction in Europe, 9% of bee and butterfly species are threatened, and populations of 37% of bees and 31% of butterflies are declining)ĭecreased pollination services during the peak period of pollination (i.e. Lower species mobility, thus decreased ability to disperse seeds. Effect of variability on services provisionĬonversion of wetlands for commercial purposes and resource extraction leads to loss of regional climate regulating function.Ĭonversion of wetlands causes the average temperature to increase by 0.77?C in all four seasons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
